
«Systems and Means of Informatics»
Scientific journal
Volume 31, Issue 4, 2021
Content | About Authors
Abstract and Keywords.
- A. A. Zatsarinny
- Yu. S. Ionenkov
Abstract: The article is devoted to the issue of assessing the quality of information systems (IS). The concepts of product quality in general and IS quality in particular are presented. The differences between the concepts of "quality" and "efficiency" are considered. The most common currently foreign and domestic models of IS quality are presented. It is noted that most of them relate to the assessment of the quality of software, while the regulatory framework for assessing the quality of IS as a whole is not sufficiently developed.
The main methods of assessing the quality of IS are considered. The proposals for improving the regulatory framework in the field of IS quality assessment are formulated.
Keywords: quality; quality assessment; quality assessment method; indicator; information system
Abstract: The article is devoted to the problem of feature selection in regression models estimated using the ordinary least squares method. Models constructed as a result of such selection are often inadequate and poorly interpreted. For the first time, the definitions of "quite interpretable" and "RTF-adequate" regression models are formulated. The previously proposed effective algorithm for solving the problem of feature selection is considered. On its basis, an algorithm has been developed for constructing quite interpretable and RTF-adequate linear regression models. In it, for each regression, the following tests are sequentially carried out: "informativeness" of variables, multicollinearity, correspondence of coefficients signs to the physical meaning of factors, adequacy of model in terms of coefficient of determination and significance in general according to Fisher's F-test, and significance of the coefficients according to the Student's t-test.
The proposed algorithm is implemented as a program for the Gretl econometric package. The developed program is universal and can be used to solve a wide range of data analysis tasks.
Keywords: feature selection; ordinary least squares; quite interpretable and RTF-adequate regression; variable "informativeness" criterion; multicollineari- ty; Fisher's F-test; Student's t-test
Abstract: The problem of analyzing a monotonic trend is considered. The model is based on the change in the mean of the normal distribution, for which the distributions of the likelihood ratio statistics are mixtures of chi-square or beta distributions with weights determined through the Stirling numbers of the first kind. The questions of approximation of these distributions are investigated. An effective method for calculating significance criteria by discarding insignificant elements of a mixture is proposed which makes it possible to reduce the complexity of calculations by several orders of magnitude. The issues of expanding the criteria for analyzing the trend of the mean normal distribution to procedures for identifying stochastic ordering are discussed. For these purposes, the authors apply the monotonic trend criterion for the averaged ranks, the statistics of which, in the absence of changes, is distributed as a mixture of chi-square distributions.
The use of a graded assessment structure was of fundamental importance: it was possible not only to obtain original results, but also to ensure the viability of the proposed solutions.
Keywords: monotone trend; likelihood ratio test; nonparametric trend detection; asymptotic distribution; probability distribution approximation
- D. N. Moldovyan
- A. A. Moldovyan
- N. A. Moldovyan
Abstract: The paper considers the use of a finite multiplicative group of invertible matrices of dimension 2 x 2 set over the field GF(p) as algebraic carrier of the digital signature schemes based on the computational difficulty of the hidden discrete logarithm problem and satisfying the general criterion of post-quantum resistance. The existence of a sufficiently large number of commutative subgroups with two-dimensional cyclicity is shown. This fact is used in the construction of a specific signature scheme which is of interest as a post-quantum cryptosystem.
In the introduced digital signature scheme, a new form of the hidden discrete logarithm problem is applied. The said form is characterized by the use of a commutative group with two-dimensional cyclicity as a hidden group and masking operations of two different types: (i) having the property of mutual commutativity with the exponentiation operation and (ii) free from this property.
To ensure the correct operation of the cryptographic scheme, a special type of verification equation is used in the signature authentication procedure, and when generating a signature, one of the elements of the latter is calculated as a root of quadratic equation.
Keywords: finite group of matrices; computationally difficult problem; discrete logarithm; digital signature; post-quantum cryptography
Abstract: When a program vulnerability is successfully exploited, the exploit often calls some system function. Therefore, one of the possible ways to detect exploitation of a vulnerability of a specific program is to check for atypical distance between the call with
the number i and the call with the number i - j where j 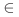 {1,..., T}, T {1,..., T}, T 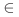 N. Distance is understood as the difference
between the addresses of the call of these functions and the typicality is determined by checking whether it belongs to the distance profile. In addition to the T parameter, the detection
algorithm uses the parameter W( N. Distance is understood as the difference
between the addresses of the call of these functions and the typicality is determined by checking whether it belongs to the distance profile. In addition to the T parameter, the detection
algorithm uses the parameter W( 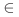 N): it is the number of profiles against which the call is checked. In this case, for j N): it is the number of profiles against which the call is checked. In this case, for j 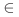 {1, . . . , W},
the profile with the number j is constructed from pairs of calls from a legitimate sequence, the difference of call indices in which is equal to j. The aim of this work is, on the one hand, to describe the detection algorithm and, on the other, to provide an experimental estimate of the sufficient values of the parameters W and T. As a result, in particular, it was found that the values of these parameters depend on the set of monitored functions; therefore, for each set of functions (and each protected program), these parameters must be found separately. {1, . . . , W},
the profile with the number j is constructed from pairs of calls from a legitimate sequence, the difference of call indices in which is equal to j. The aim of this work is, on the one hand, to describe the detection algorithm and, on the other, to provide an experimental estimate of the sufficient values of the parameters W and T. As a result, in particular, it was found that the values of these parameters depend on the set of monitored functions; therefore, for each set of functions (and each protected program), these parameters must be found separately.
Keywords: software vulnerabilities; distance between function calls; program protection
- S. B. Rumovskaya
- I. A. Kirikov
Abstract: The study of the cognitive structures and mechanisms of a specialist (doctor) will make the processes of overcoming the diagnostic problem visible and contrasting. Systems with cognitive modeling of the diagnostic problem developed on their basis will reduce the number of medical errors and improve the quality of medical decision support systems. The paper considers the cognitive hybrid intelligent diagnostic system, its subject-visual model, and typical architecture as well as the features of laboratory testing by the example of the problem of diagnosing diseases of the pancreas.
Keywords: cognitive hybrid intelligent diagnostic system; individual diagnostic decision making; cognitive image of the diagnostic object; operational images of the diagnostic object
- D. V. Khilko
- Yu. A. Stepchenkov
- Yu. I. Shikunov
- Yu. G. Diachenko
- G. A. Orlov
Abstract: The paper covers the fast Fourier transform (FFT) support in the hybrid recurrent signal processor architecture. An analysis of the existing implementation is presented. Disadvantages and their ramifications are identified. An optimized solution is proposed to ease the scaling of both the architecture and the number of FFT samples.
Keywords: digital signal processing; fast Fourier transform; digital signal processor; Radix-2
Abstract: Two models of generating new knowledge are compared. The first, the spiral model, describes the processes of generating new knowledge in the economic sphere. The second model is used in computational linguistics and medical informatics. This model focuses on the design of information technologies and automated systems that ensure the generation of new knowledge during the semantic analysis of texts (referred to as the information technology-oriented model, or ITO model). The comparison of the two models is presented as a step- by-step transformation of the spiral model into the ITO model. The primary purpose of the paper is to describe four stages of transformation. At the first stage, mental and informational media are separated in the spiral model. Then, at the second stage, a digital medium is added to them with potential sources of new knowledge in the form of a database of text data corresponding to the goal of knowledge discovery from texts. The reference sample of the novelty of the discovered knowledge is being set. At the third stage, a list of eight processes of generating new knowledge is formed. A knowledge base is being added for storing forms of representation of concepts of newly discovered knowledge. The transformation of the spiral model into the ITO model is completed at the fourth stage by integrating eight processes of generating new knowledge. The stages of transformation are illustrated by an example of discovering new knowledge about the meanings of German modal verbs.
Keywords: spiral model; generation of new knowledge; ITO model; semantic analysis of texts; transformation of the spiral model
- A. V. Borisov
- A. V. Bosov
- D. V. Zhukov
- A. V. Ivanov
Abstract: In the third article of a series, devoted to the description of the decision support system in the field of ensuring the safety of passenger traffic and countering illegal activities in transport, the conceptual model proposed in the first article of a series and supplemented by the basic functional content in the second article of a series is expanded with specialized analytical statements. Firstly, a set of formal concepts is formed that provide the possibility of transforming the operational tasks of the system users into computational tasks for the selected transport data. Then, a series of computational problems is presented that provide information support for the analyst of the subject area in solving operational problems, analyzing incidents, and conducting situational analysis. Finally, a planned presentation of analytical functions associated with complex data processing is announced.
Keywords: transport safety; decision support system; design problem; transport information; route of travel; transport area
- A. V. Borisov
- A. V. Bosov
- D. V. Zhukov
Abstract: The article continues the cycle of works devoted to the analysis of the impact of public administration on the effectiveness of research and development in the field of artificial intelligence (AI R&D). The third part of the cycle is a study of government influence on AI R&D using the United States as an example. A brief description of the U.S. strategic document in the field of AI R&D is given including a compact statement of its goals and objectives as well as implementation principles. In addition, a related document of the US Department of Defense was analyzed. A classification analysis of AI R&D directions in the field of defense and security carried out by the main specialized research organizations of the United States is presented.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI); US Department of Defense (DoD); Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA); Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Agency (IARPA)
- A. A. Grusho
- D. V. Smirnov
- E. E. Timonina
- S. Ya. Shorgin
Abstract: Tokenization is one of the methods of depersonalizing personal data.
This method is a bijective replacement of fragments of personal data with random elements of a certain set. One of the weaknesses of personal data protection through tokenization is the possibility of statistically assessing the probabilities of the occurrence of protected fragments of personal data. The paper proposes a method of enhancing tokenization algorithms which allows overcoming this weakness. The enhanced tokenization algorithm is slightly different in complexity from other algorithms. At the same time, the enhanced algorithm can be used both in cases of tokenization by replacing alphabets describing various fragments of personal data and in cases where personal data are divided into fragments of the same length and converted into fragments of the same length but in other alphabets.
Keywords: information security; depersonalization of personal data; tokenization; mathematical statistics
- V. A. Beschastnyi
- D. Yu. Ostrikova
- V. S. Shorgin
- D. A. Moltchanov
- Yu. V. Gaidamaka
Abstract: Terahertz (THz) band is considered as the main candidate for new radio access technology in sixth-generation (6G) cellular systems. Requiring large antenna arrays at base station (BS) and user equipment (UE) sides to compensate for extreme path losses, THz systems will utilize extremely directional antenna radiation patterns. As a result, the performance of these systems will be severely affected by not only blockage but also UE micromobility in hands of a user.
The negative effects of these phenomena can be alleviated by utilizing the multiconnectivity functionality that allows UE to maintain two or more links to nearby BSs and use them when the currently active link is lost. By accounting for THz specific propagation, antenna and beam searching design, the density of THz BS deployment, and multiconnectivity operation, the successful session completion probability under both types of impairments has been investigated.
The present results indicate that the gains of multiconnectivity are observed up to 5 simultaneously supported links and heavily depend on the application outage tolerance time and are mostly affected by micromobility. To improve it, one needs to ensure that the application may tolerate outage caused by beam searching time which is of the order of milliseconds.
Keywords: terahertz communications; micromobility; outage; multiconnectivity; human body blockage; beam searching
- I. M. Adamovich
- O. I. Volkov
Abstract: The article is devoted to the further development of the distributed technology of concrete historical investigation support based on the principles of crowdsourcing and focused on a wide range of users which are nonprofessional historians and biographers. Development is carried out through the automation of one of the main types of Internet searches (indirect Internet search) used in biographical research. The article analyzes the possible approaches to the automation of Internet search taking into account the specifics of concrete historical investigation. The use of web-crawlers is substantiated and the requirements for them arising from the distinctive of this technology are formulated. The possibility of using ready-made solutions is estimated. The necessary changes in the object model of the technology and the modifications of its algorithms related to indirect Internet search are described. As an additional measure to reduce the difficulty of indirect Internet search, the new mechanism for automating of the interaction of the technology users which execute their investigations in similar directions is proposed and described in detail.
Keywords: concrete historical investigation; distributed technology; web- crawler; data model; Internet search
Abstract: Power-coordination status systems have been defined and the dependence of their effectiveness on the excellence of the applied information technologies has been substantiated. The necessity of a planned change in the structure of such systems is substantiated as the methods and means of implementing information technologies are improved. Examples are given that demonstrate the relationship between the level of management efficiency and the level of perfection of the software and hardware implementing organizational and information support of the public administration system. Special attention is paid to informational feedback and notification of the population about state laws and their implementation.
Keywords: power-coordination systems; relations of subordination and coordination; information technology; mechanism of state administration; digital platforms
|



 {1,..., T},
{1,..., T},