
|

«Systems and Means of Informatics»
Scientific journal
Volume 23, Issue 2, 2013
Content | About Authors
Abstract and Keywords.
COVERT CHANNELS GENERATED BY TAGS IN DATAGRAMS.
- A. A. Grusho IPI RAN; M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia,
grusho@yandex.ru
- N.A. Grusho IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, info@itake.ru
- E. E. Timonina IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, eltimon@yandex.ru
Abstract: The covert channels generated by tags are defined by separation in a
data stream of sections which lengths are the codes of hidden transmitted data. Separation of sections of data is carried out with the help of tags. It is simpler to
hide tags from detection, or it is possible to transfer them on other channel. In the
paper, such covert channels are described by a couple of synchronized processes.
The considered method of the hidden transmission allows to transfer large amount
of hidden information in case of minor changes in a legal data stream. Examples of
such covert channels are given. The correctness of coding and decoding of hidden
information in such channels is proved. Such covert channels can be used not
only for hidden information transfer, but also for integrity monitoring.Methods
of creation of proved invisible tags for such channels are found. Invisibility is
provided with cryptography methods. Implementation ability of the considered
methods is confirmed experimentally. The computer prototype for experiments
uses only the open software.
Keywords: covert channels; integrity monitoring; invisibility of the covert
channels; transfer protocols of datagrams
TOPOLOGICALMODEL OF FINGERPRINT IMAGE.
- V. Yu. Gudkov Chelyabinsk State University, Chelyabinsk, Russia, diana@sonda.ru
- O. S. Ushmaev IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, oushmaev@ipiran.ru
Abstract: The paper describes a new fingerprint image model which consists
of topological and geometrical features of minutiae neighborhoods. To create a
model, the authors suggest to calculate the topological features in the neighborhood
of each fingerprint minutiae: ridge ending or bifurcation. The topological
feature is the interrelation between two minutiae. An example of topological
feature is the fact that two minutiae are situated on one ridge. Then, the list
of topological features is constructed. Description of each feature is extended
with metric information: distances between minutiae. Further, the proposed
model is used for fingerprint identification. The experiments have shown that
simultaneous usage of topological and metric features significantly improves the
accuracy of fingerprint identification. On public available databases FVC2004,
at FMR = 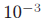 , FNMR is 2%. , FNMR is 2%.
Keywords: topological vectors; events; bond length; fingerprint; identification
METHOD OF PARALLEL CIRCUITS FOR FINGERPRINT IMAGE RECOGNITION.
- V. Yu. Gudkov Chelyabinsk State University, diana@sonda.ru
Abstract: New method of fingerprint image processing is described. The method
is based on simultaneous tracking of ridges and valleys directions, instead of tracking ridges. In areas of good quality, the directions can be determined
confidently both for ridges and valleys. But in areas of poor quality, there is
a problem with accurate measuring of ridge flow. Given a pixel on filtered
fingerprint image, the chains of pixels of minimal and maximal intensity are
tracked. Based on the results of tracking, the hypotheses on ridge flow direction
for ridges and valleys are generated. Then, the results are fused in order to obtain
estimation of ridge flow direction and density. It allows to significantly improve
the accuracy of ridge flow direction and density in the areas of poor quality.
Finally, it is used to form the field of flows and its confidential (quality) matrix.
More accurate measuring of ridge direction improves fingerprint recognition by
more accurate feature extraction: ridge endings and bifurcations.
Keywords: fingerprint; field of flows; chiaroscuro; parallel circuits
PERSON CLASSIFICATION UPON FACE IMAGE BASED ON SIMILE CLASSIFIERS.
- V. S. Konushin M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, vadim@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- T.M. Lukina M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, tlukina@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- A. I. Kuharenko M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, akuharenko@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- A. S. Konushin M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, ktosh@graphics.cs.msu.ru
Abstract: A new approach to person classification upon face images is presented.
It consists of two steps. First, similarity distances between a test face and faces
from a known sample are computed. For this task, special simile classifiers are
trained. Similarity distances are estimated independently for each face fragment,
e. g., nose, mouth, left or right eye, etc. Pixel colors, brightness, gradient norm, and orientation are used as features both for each pixel and for whole
fragment in the form of a histogram or Gaussian distribution parameters. Person
classification is performed based on these similarity distances. For classification,
support vector machine with radial basis function kernel is used. The proposed
algorithm was tested on a gender classification task, using Labeled Faces in
the Wild and Public Figures Face databases. The algorithm achieved 92.96%
accuracy.
Keywords: face classification; gender classification; support vector machine
AGE ESTIMATION UPON FACE IMAGE BASED ON LOCAL BINARY PATTERNS AND A RANKING APPROACH.
- A. V. Rybintsev M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, arybintsev@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- T.M. Lukina M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, tlukina@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- V.S. Konushin M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, vadim@graphics.cs.msu.ru
- A. S. Konushin M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, ktosh@graphics.cs.msu.ru
Abstract: A new age classification algorithmis suggested, which is a modification
of method developed by Chang et al. The algorithm is based on training of a
set of binary classifiers. Each classifier estimates whether the person is older
than a specified age or not. The age then can be simply calculated as a sum
of outputs of all binary classifiers. Using local binary patterns as classification
features, age prediction accuracy improvement is achieved, though classifier
size is increased. A number of modifications, which decrease a classifier size
and increase classification speed, but keep age estimation accuracy high, are
proposed. Experiments on MORPH database showed mean absolute error from
4.52 to 5 years and classification time between 0.32 and 3.21 s, depending on
parameters.
Keywords: face classification; age classification; local binary patterns
THE SEARCH FOR MATCHES BETWEEN THE IRIS KEY POINTS
USING HERMITE PROJECTION PHASE - ONLY CORRELATION METHOD.
- E. A. Pavelyeva Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow
State University, Moscow, Russia, paveljeva@yandex.ru
Abstract: The paper is based on the analysis and comparison of the iris key
points which are the most informative points of the iris image texture. The key points are selected using Hermite transform. The search for matches between
the iris key points using Hermite projection phase-only correlation of local areas
around key points is suggested. In Hermite projection phase-only correlation
method, the Fourier transform is applied to the expansions of images intensity
functions in a Fourier series of Hermite functions. The proposed method of key
points comparisons does not use any information about key points locations, is
robust to eyelids, eyelashes, and glares, and gives good results.
Keywords: iris recognition; phase only correlation; Hermite functions; key
points; biometrics
DISCRIMINANT ANALYSIS FOR CLASSIFICATION
AND FORECASTING OUTCOMES OF THE TREATMENT.
- M. A. Dranitsyna M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Faculty of Computational Mathematics
and Cybernetics, Moscow, Russia, margarita13april@mail.ru
- T. V. Zakharova M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Faculty of Computational Mathematics
and Cybernetics, Moscow, Russia, lsa@cs.msu.ru
Abstract: The aim of the work was to develop a classification method for
patients underwent hyperbaric oxygenation procedure and to build up a relevant
mathematical model of evaluation and forecasting the patient condition during
each session and the whole therapy course. This classification method supposed
to be based on the effectiveness of the treatment. The group of 161 patients
was observed. For each patient, cardiac physiological parameters were registered
during each hyperbaric oxygenation session via continuous computer monitoring
system. The discriminant analysis was applied to obtained data. In the model
developed, the rate of success in test sample classification achieved 75%. The
classification technique based on statistical inference and expert estimates was
developed.
Keywords: discriminant analysis; discriminant variables; classification functions;
forecasting
STUDY OF THE COMPLEX PROBLEMOF ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSTICS IN THE METHODOLOGY OF ARTIFICIAL HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS.
- I. А. Kirikov The Kaliningrad Branch of the Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian
Academy of Sciences, Kaliningrad, Russia, baltbipiran@mail.ru
- А.V. Kolesnikov The Kaliningrad Branch of the Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian
Academy of Sciences; Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, Kaliningrad,
Russia, avkolesnikov@yandex.ru
- S. B. Rumovskaya The Kaliningrad Branch of the Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian
Academy of Sciences, Kaliningrad, Russia, sophiyabr@gmail.com
Abstract: An approach to modeling the decision-support systems within the
methodology of artificial heterogeneous systems is introduced on an example
of a complex problem of the arterial hypertension diagnostics. Investigations
were conducted on two models: \heterogeneous" and \homogeneous," and are
relevant to the new scientific worldview in biomedicine, based on principles of
variety, complementarity, cooperation, and relativity. The aim of the research is
to develop the consulting hybrid intelligent system for the arterial hypertension
diagnostics. The results of system analysis of the complex problem of arterial
hypertension diagnostics within the methodology of artificial heterogeneous
systems are presented, namely, identification and reduction of the complex
problem, subtasks specification, methods selection for solving of homogeneous
subtasks, and proof of the problem heterogeneity.
Keywords: decision-support system; functional hybrid intelligent system;
heterogeneous problem; arterial hypertension diagnostics
AGGREGATION GEOCONCEPTS FOR GENERALIZATION MAPS,
APPROPRIATE LOGICAL CONSISTENCY AND SEMANTIC ACCURACY.
- S. K. Dulin IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, s.dulin@ccas.ru
- N.G. Dulina Dorodnicyn Computing Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia,
ngdulina@mail.ru
- P. V. Ermakov IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, petcazay@gmail.com
Abstract: In recent years, the number of fixed and mobile devices using
automated methods of generalization map dramatically increased. This raises the
question of the quality of digital imaging models map. Generalization should
not only ensure certain standards for the derived scale of the map, but also
maintain a certain level of semantics. To conduct an objective comparison of the
different results of generalization, it is necessary to introduce a measure of the
accuracy of semantic aggregation areas and geoconcepts. An approach that shows
how this could be used to compare the results of generalization is presented.
Also, the methods for determining the relationship between n geoconcepts to be
distributed over N units so that in each unit, therewere geoconcepts most similar
to each other on the set of m selected descriptive features. The function F is
introduced | a similarity geoconcepts function of jointly k selected features,
normalized to the maximum range of the characteristic values on the set of n
geoconcepts.
Keywords: generalization; the quality of geodata; aggregation of the map areas;
aggregation of geoconcepts
THEORETICAL ASPECTS OF PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY
DEVELOPMENT FOR RECURRENT ARCHITECTURE.
- D. Khilko IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, dhilko@yandex.ru
- Yu. Stepchenkov IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, YStepchenkov@ipiran.ru
Abstract: The paper is dedicated to a new recurrent dataflow computational
paradigm and the methodology intended for solving and programming of
corresponding problems. These problems are meant to be solved with the computational
device that is being developed, which architecture is based on ideas
and principles of proposed paradigm. Also, its realization in multicore dataflow
recurrent architecture is suggested. Recurrent organization of computational
process is theoretically proven to converge by using terms and theorems of the
recursive functions theory. The software engineering problemfor this architecture
is described and its solution| recurrent dataflow programming methodology|
is suggested. This methodology is demonstrated on a problem of isolated words
recognition with device based on a new architecture. Also, one of the basic
algorithms of the mentioned problem | band-pass filtering | is realized by
using the proposed methodology step by step.
Keywords: computational paradigm; programming methodology recursiveness;
dataflow architecture
METHODOLOGICAL QUESTIONS OF FORMATION OF THE SYSTEM TECHNICAL SUPPORT
OF INFORMATION - TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS.
- A. A. Zatsarinnyy IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, azatsarinny@ipiran.ru
- N.G. Buromenskii Branch of the Federal State Government Institution "46 Central Reserach Institute
of Defence Ministry of Russia", Mytishchi, Russia, buromienskii@mail.ru
- A. I. Garanin IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, algaranin@mail.ru
Abstract: The basic concepts in relation to the object of research are described. It
is shown that the formation of the system of technical support (STS) of information
and telecommunication network (ITN) is an integrated system problem, acquiring preconceptual covering of a very wide range of interrelated processes at all
stages of the life cycle of ITN. Basic of them are formulated almost in the
same sequence as they should be resolved in the course of creation of the STS.
Consistently, the stages of research to create an STS, the tasks, and obtained
results are described. The analytical model of the functioning of the STS and
general scheme of the method of forming the STS are given. It is shown that the
mathematical description of the processes of functioning of complex hierarchical
systems, such as STS of ITN, is extremely complex and serious problem. Its
solution is suggested in two stages: at the first stage, the description is given
in the form of abstract mathematical formalization of the process of functioning
with the use of set theory (relations on the set between sets and functional
maps), and at the second stage, the most important processes in the system, such
as repair, maintenance, supply of new technical means, spare parts tools and
accessories are distinguished and transition from intuitive concepts to detailed
mathematical description of using analytical and probabilistic models is realized.
An approximate structural scheme of the STS is suggested. Basic content of the
regulatory support of the STS of ITN is justified.
Keywords: system; information and telecommunications system; the system
of technical support; research; design; development; operation; effectiveness;
modeling; structure
ON A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SITUATIONAL CENTERS EFFICIENCY.
- A. A. Zatsarinnyy IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, azatsarinny@ipiran.ru
- Y.S. Ionenkov IPI RAN, uionenkov@ipiran.ru
- A. P. Shabanov IPI RAN, apshabanov@mail.ru
Abstract: The issues of performance evaluation of situational centers that solve
similar problems are considered. The consideration is based on structural and
functional representation of a situational center taking into account institutional
components and human factors. Principle of comprehensive evaluation is used.
This principle consists in the fact that operational efficiency of situational centers
is defined by efficiency indexes of its components - functional, technological,
technical, exploitative and organizational ones. The system of efficiency indexes
of each component is suggested. Atechnique of comparative analysis of situational
centers efficiency and examples of its calculation are presented. It is shown
that development and integration of high-performance systems which provide
execution of full list of required tasks even with creation of necessary technical
infrastructure will not allow to achieve high level efficiency of situational center
if exploitative and organizational components are at low level.
Keywords: situational centers; efficiency; indicators
FORMATION OF THE GOALS SYSTEM FOR SITUATIONAL CONTROL.
- A. P. Suchkov IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, asuchkov@ipiran.ru
Abstract: The basic principles of structure, content, and implementation of the
system of goals in the management real-time systems, connected with a situational
analysis, are discussed. Well-known criteria SMART is used to check the
effectiveness of goal-setting in control systems and formalization of the OODA cycle management. In accordance with the chosen ways of formalization, the
model list of essential management purposes is formed by sections of observation,
orientation, decision, and action. The issues of specifying thegoals, quantitative
evaluation of their achievements, and the generalized criteria of efficiency of
management on the basis of situational analysis are discussed. It is shown that the
quantitative indicators of the degree of implementation of goals must be based on
a combination of objective indicators of management and methods of expert and
statistical estimation of parameters of the external environment.
Keywords: management system; situational analysis; system of goals
UNIVERSAL PATTERN OF ORGANIZATIONS FOR THE SITUATIONAL CENTERS.
- A. V. Kolesnikov Baltic Federal University named after Kant, Kaliningrad Branch of IPI RAN,
Kaliningrad, Russia, avkolesnikov@yandex.ru
- А. А. Merkulov Baltic Federal University named after Kant, Kaliningrad, Russia,
alex.merkulov@mail.ru
Abstract: Interdisciplinary technology of modeling organizational structures,
based on the approaches technetika, organizational cybernetics, and principles
of autopoiesis is presented. Developed an invariant pattern of modeling - VSM (Viable System Model) Cenose which is presented in the form of an
abstract model and the platform for engineering situational centers based on it.
Platform «Situational Centre "VSM Cenose" » can be used for organizations of
different types, forms of ownership, methods of accounting, size, complexity,
and other parameters. The mechanism of pattern projection from the meta
model is developed through an abstract and specific model of the landscape of
the organization. The advantages of design and management on the basis of a
unified information environment allowing to move freely through all levels of
hierarchically organized structures and to maintain overall control of the situation
without loss of activity have been shown. This technology is scalable from a
small organization to the level of the city, industry, and country.
Keywords: pattern; synthesis; technetica; organizational cybernetics; autopoiesis;
organization; VSM Cenose; situational center
SITUATIONAL CENTER VSM CENOSE.
- A. V. Kolesnikov Baltic Federal University named after Kant, Kaliningrad Branch of IPI RAN,
Kaliningrad, Russia, avkolesnikov@yandex.ru
- А. А. Merkulov Baltic Federal University named after Kant, Kaliningrad, Russia,
alex.merkulov@mail.ru
Abstract: The description of the platform «Situational Center VSM Cenose»,
aimed at configuring and operating of a situational center in the organizational structures of various forms of ownership and activities. Main functions: display
of internal and external environment due to specialized multidimensional and
multifactor graphical interface; display of forecasting information; combining
different ways of description; presentation of information in accordance with
the principles «from the general to the specific», «top-down» invariance with
the respect to changes in the way of accounting methods, forms of business
organization due to complex organization based on the basis ideas of technetika
and organizational cybernetics; expanding the functionality of the complex
during the operation due to the migration process templates, both between levels
of the organizational structure and the different systems due to meeting the
principles of recursion, self-similarity and fractal; and interchange of data with
third-party program developers. The specific feature is the technology «VSM
Cenose», which makes situational center «VSM Cenose» a universal platform
for replicability of situational centers.
Keywords: situational center; platform; VSM Cenose pattern
DATA PREPROCESSING AND EXTRACTION OF LOGICAL RULES BASED ON THE GENETIC ALGORITHM.
- V. N. Gridin Center of Information Technologies in Design, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Odintsovo, Moscow Region, Russia, info@ditc.ras.ru
- V. I. Solodovnikov Center of Information Technologies in Design, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Odintsovo, Moscow Region, Russia, info@ditc.ras.ru
Abstract: The possibility of joint use of genetic algorithms and methods
for extraction of logical rules in data mining problems is considered. The
combined data preprocessing algorithm is suggested. It consists in segmentation
and selection of the most significant values of attributes and combinations of
attributes using the genetic algorithm. It can be attributed to the so-called island
algorithms as the number of populations is selected equal to the number of classes.
Choosing such quantity of populations is due to the fact that the performance
assessment of the rules accuracy and completeness is appropriate to produce for
each class. It is shown that the genetic algorithm allows selection of logical rules in the multivariate data analysis with high accuracy and completeness. The
presented algorithm can be used to analyze data in data warehouses to detect
hidden patterns in them, on the basis of which the construction of rules and
decision trees could be produced.
Keywords: genetic algorithm; logical rule; data mining
INFORMATION SYSTEM CONCEPTUAL DECISIONS
FOR ASSESSMENT OF LINKAGES BETWEEN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGIES.
- V. A. Minin Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Moscow, Russia, minin@rfbr.ru
- I.M. Zatsman IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, iz ipi@a170.ipi.ac.ru
- V. A. Havanskov IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, havanskov@a170.ipi.ac.ru
- S. K. Shubnikov IPI RAN, Moscow, Russia, sergeysh50@yandex.ru
Abstract: The description of conceptual decisions for assessment of linkages
between science and technologies is considered. The decisions are a framework
for developing information systems, which will have some new features. These
features are not present in other similar information systems of the Russian
scientific and technical sphere. Their development is necessary for monitoring
and evaluating R&D programs and decision-making at all stages of scientific
and technical program activities. The architecture as a whole system and
conceptual decisions on separate functional subsystems are described. These
decisions are based on methodology for assessment of linkages between science
and technologies, which is developed in IPI RAN. Conceptual decisions have a
number of fundamental differences from other systems for assessment of linkages
between science and technologies. First, there is a possibility of fetching a system
for classification of knowledge domains fromsome classification systems. Second,
formation and application of terminological portraits for headings of the chosen
classification system is provided.
Keywords: monitoring and evaluating of programs; linkages between science
and technologies; methodology for assessment of linkages; information systems;
conceptual decisions
DATABASE «FORC STAFF PROCEEDINGS» AS A PART
OF THE «FIBER OPTICS INFORMATION SYSTEM».
- T. A. Kochergina Fiber Optics Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FORC RAS),
Moscow, Russia, tatyanan@fo.gpi.ru
- L.D. Iskhakova Fiber Optics Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FORC RAS),
Moscow, Russia, ldisk@fo.gpi.ru
- N. E. Kalenov Library for Natural Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia,
nek@benran.ru
- M. M. Yakshin Library for Natural Sciences, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia,
greycat.na.kor@gmail.com
Abstract: The paper describes Fiber optics information system (IS). Its purpose
is to provide scientific digital resources for basic and applied research in this
area. Information system allows users to have access to bibliographic information
and full texts of articles. Access to full-text articles is carried out using the
appropriate links to the site publishers (if user has a subscription). Content of
IS is being provisioned by experts using scientific databases and FORC staff
publications. The main possibilities of IS software and some practical examples
are considered. The section of IS, which is called «Proceedings FORC» and
practical approaches when working with the database (DB) are shown. The
characterization of the content DB «Proceedings FORC» is described. The
results of some bibliometric research on the quoting of the FORC are presented.
Keywords: database; fiber optics; information technology; scientific electronic
resources
|

|



