
|

«INFORMATICS AND APPLICATIONS»
Scientific journal
Volume 8, Issue 2, 2014
Content | About Authors
Abstract and Keywords.
ANALYTICAL MODELING OF DISTRIBUTIONS WITH INVARIANT MEASURE IN NON-GAUSSIAN DIFFERENTIAL AND REDUCABLE TO DIFFERENTIAL HEREDITARY STOCHASTIC SYSTEMS.
- I. N. Sinitsyn Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Abstract: Exact and approximatemethods and algorithms of one- and multidimensional distributions with invariant
measure for analytical modeling in differential non-Gaussian (with Wiener and Poisson noises) stochastic systems
(StS) and hereditary StS (HStS) reducible to differential are presented. Four theorems giving exact methods of
analysismodeling in differential StS (DStS) of general type are proved. Approximatemethods based on distributions
parametrization in DStS are disscused. Special attention is paid to the methods of normal approximation (MNA)
and statistical linearization (MSL) for one- and dimensional distributions in DStS. Stability conditions are
presented. three theorems giving exact and approximate analytical modeling in HStS resucible to DStS with
asymptotically dying kernels are given. Some equavalency applications of DStS and HStS are considered. Test
examples for software tools “ID StS” are given.
Keywords: analytical modeling; differential stochastic system; distribution with invariant measure; Gaussian
(normal) stochastic system; hereditary kernel; hereditary stochastic system; hereditary system reducible to
differential; Ito stochastic differential equation; method of statistical linearization; non-Gaussian (withWiener and
Poisson noises) stochastic system; normal approximation method; singular kernel; software tools “ID StS”
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF Geo/Geo/1/R QUEUE WITH HYSTERETIC LOAD CONTROL.
- A. V. Pechinkin Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation, Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia, 6 Miklukho-Maklaya Str., Moscow 117198, Russian Federation
- R. V. Razumchik Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Abstract: Threshold load control is one of the key techniques to prevent overloads in telecommunication networks.
Its variants are used for overload detection in signalling system No. 7 as well as in next generation networks where
session initiation protocol (SIP) is the main signalling protocol. Consideration is given to discrete-time
Geo/Geo/1/R queueing system which is one of the possible mathematical models of the SIP proxy-server.
Bi-level hysteretic load control is implemented in the system. The methods that allow one to obtain a stationary
joint probability distribution of the number of customers in a system and system’s state, stationary waiting and
sojourn time distributions, and distribution of first passage times from different system’s states are presented.
A numerical example based on obtained analytical expressions is given.
Keywords: queueing system; discrete time; hysteretic load control; performance characteristics
ON THE OVERFLOW PROBABILITY ASYMPTOTICS
IN A GAUSSIAN QUEUE.
- O. V. Lukashenko Institute of Applied Mathematical Research, Karelian Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, 11 Pushkinskaya Str., Petrozavodsk 185910, Russian Federation
Petrozavodsk State University, 33 Lenin Str., Petrozavodsk 185910, Russian Federation
- E. V. Morozov Institute of Applied Mathematical Research, Karelian Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, 11 Pushkinskaya Str., Petrozavodsk 185910, Russian Federation
Petrozavodsk State University, 33 Lenin Str., Petrozavodsk 185910, Russian Federation
- M. Pagano University of Pisa, 43 Lungarno Pacinotti, Pisa 56126, Italy
Abstract: Gaussian processes are a powerful tool in network modeling since they permit to capture the long memory
property of actual traffic flows. In more detail, under realistic assumptions, fractional Brownian motion (FBM)
arise as the limit process when a huge number of on-off sources (with heavy-tailed sojourn times) are multiplexed
in backbone networks. This paper studies fluid queuing systems with a constant service rate fed by a sum of
independent FBMs, corresponding to the aggregation of heterogeneous traffic flows. For such queuing systems,
logarithmic asymptotics of the overflow probability, an upper bound for the loss probability in the corresponding
finite-buffer queues, are derived, highlighting that the FBM with the largest Hurst parameter dominates in the
estimation. Finally, asymptotic results for the workload maximum in the more general case of a Gaussian input
with slowly varying at infinity variance are given.
Keywords: Gaussian fluid system; overflow probability; logarithmic asymptotics
THE GENERALIZED PROBLEM OF SOFTWARE SYSTEM RESOURCES DISTRIBUTION .
- A. V. Bosov Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Abstract: The paper presents the statement and the solution of the optimization problem for a dynamic system
with a linear output and the quadratic performance criterion. System uncertainty is described by the observed
second-order stochastic process. The need to optimize resource distribution of software systems gives practical
justification to the problem. In such interpretation, the uncertainty of a systemdescribes user activity and the output
describes running queries or the volume of the requested memory. The goals of optimization are formalized by
the quadratic performance criterion of the general form. The criterion, in particular, summarizes two problems of
resource distribution of software systems discussed earlier. The objective functional makes it possible, in particular,
to state the problem of adequate program resources allocation (of threads, memory, etc.), penalizing for unlimited
spending. To solve the problem, the method of dynamic programming is used. The optimal strategy is a linear
combination of the output and state predictions up to the control horizon. In the context of computational
complexity of the optimal strategy, the possibility of its simplicity and of using the locally-optimal strategy is
discussed.
Keywords: software system; stochastic observation system; quadratic criterion; dynamic programming
BAYESIAN RECURRENT MODEL OF RELIABILITY GROWTH:
BETA-DISTRIBUTION OF PARAMETERS.
- Iu. V. Zhavoronkova KM Media Company, 8/2 Prishvina Str., Moscow 127549, Russian Federation
- A. A. Kudryavtsev Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 1-52 Leninskiye Gory, GSP-1,Moscow 119991, Russian Federation
- S. Ya. Shorgin Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Abstract: One of the topical problems of modern applied mathematics is the task of forecasting reliability
of modifiable complex information systems. Any first established complex system designed for processing or
transmission information flows, as a rule, does not possess the required reliability. Such systems are subject to
modifications during development, testing, and regular functioning. The purpose of such modifications is to
increase reliability of information systems. In this connection, it is necessary to formalize the concept of reliability
of modifiable information systems and to develop methods and algorithms of estimating and forecasting various
reliability characteristics. One approach to determine system reliability is to compute the probability that a signal
fed to the input of a system at a given point of time will be processed correctly by the system. The article considers
the exponential recurrent growth model of reliability, in which the probability of system reliability is represented as
a linear combination of the “defectiveness” and “efficiency” parameters of tools correcting deficiencies in a system.
It is assumed that the researcher does not have exact information about the system under study and is only familiar
with the characteristics of the class from which this system is taken. In the framework of the Bayesian approach, it
is assumed that the indicators of “defectiveness” and “efficiency” have beta-distribution. Average marginal system
reliability is calculated. Numerical results for model examples are obtained.
Keywords: modifiable information systems; theory of reliability; Bayesian approach; beta-distribution
A METHOD OF PROVING THE OBSERVATIONAL EQUIVALENCE
OF PROCESSES WITH MESSAGE PASSING .
- A. M. Mironov Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119333, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Russian Federation
Abstract: The article deals with the problem of proving observational equivalence for the class of computational
processes called the processes with message passing. These processes can execute actions of the following forms:
sending or receiving the messages, checking the logical conditions, and updating the values of internal variables of
the processes. The main result is the theorem that reduces the problem of proving observational equivalence of a
pair of processes with message passing to the problem of finding formulas associated with pairs of states of these
processes, satisfying certain conditions that are associated with transitions of these processes. This reduction is a
generalization of Floyd’s method of flowchart verification, which reduces the problem of verification of flowcharts
to the problem of finding formulas (called intermediate assertions) associated with points in the flowcharts and
satisfying conditions, corresponding to transitions in the flowcharts. The method of proving the observational
equivalence of processes with message passing is illustrated by an example of sliding window protocol verification.
Keywords: verification; processes with message passing; observational equivalence; sliding window protocol
ON POLYNOMIAL TIME COMPLEXITY OF ULTRAMETRIC VERSIONS OF CERTAIN NP-HARD PROBLEMS .
- M. G. Adigeev Southern Federal University, 105/42 Bol’shaya Sadovaya Str., Rostov-on-Don 344006, Russian Federation
Abstract: The paper deals with important special cases of the travelling salesman problem and the Steiner tree
problem. Both of these problems are NP-hard even in the metric case, i. e., for graphs whose edge cost function
meets the triangle inequality. Even more severe restriction is imposed by the strong triangle inequality:
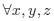
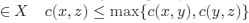
The function which meets this inequality is called ultrametric. The analysis
of graphs with an ultrametric edge cost function is presented. This analysis leads to an algorithm for building the
minimal cost Hamiltonian cycle in time 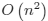 where n is the number of vertices. For the Steiner tree problem, it
is proven that in the case of an ultrametric edge function, the minimumSteiner tree includes only terminal vertices
and thus may also be constructed in polynomial time, as a minimum spanning tree on a subgraph of the original
graph.
where n is the number of vertices. For the Steiner tree problem, it
is proven that in the case of an ultrametric edge function, the minimumSteiner tree includes only terminal vertices
and thus may also be constructed in polynomial time, as a minimum spanning tree on a subgraph of the original
graph.
Keywords: ultrametric function; strong triangle inequality; travelling salesman problem; Steiner tree; polynomialtime
algorithms
INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR THE INVERSE
PROBLEM IN THE MULTIDIPOLE MODEL OF MAGNETOENCEPHALOGRAM’S SOURCES .
- V. E. Bening Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 1-52 Leninskiye Gory, GSP-1, Moscow 119991, Russian
Federation
Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian
Federation
- M. A. Dranitsyna Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 1-52 Leninskiye Gory, GSP-1, Moscow 119991, Russian
Federation
- T. V. Zakharova Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 1-52 Leninskiye Gory, GSP-1, Moscow 119991, Russian
Federation
- P. I. Karpov Department of Theoretical Physics and Quantum Technologies, College of NewMaterials and Nanotechnology,
National University of Science and Technology “MISiS,” 4 Leninskiy Prosp.,Moscow, Russian Federation
Abstract: This paper is devoted to a challenging task of brain functional mapping which is posed due to the
current techniques of noninvasive human brain investigation. One of such techniques is magnetoencephalography
(MEG) which is very potent in the scientific and practical contexts. Large data retrieved from the MEG procedure
comprise information about brain processes. Magnetoencephalography data processing sets a highly ill-posed
problem consisting in spatial reconstruction of MEG-signal sources with a given accuracy. At the present moment,
there is no universal tool for accurate solution of such inverse problem. The same distribution of potentials on the
surface of a human head may be caused by activity of different areas within cerebral cortex. Nevertheless, under
certain assumptions, this task can be solved unambiguously. The assumptions are the following: signal sources are
discrete, belong to distinct functional areas of the brain, and have superficial location. The MEG-signal obtained
is assumed to be a superposition of multidipole signals. In this case, the solution of the inverse problem is a
multidipole approximation. The algorithm proposed assumes two main steps. The first step includes application
of independent component analysis to primary/basic MEG-signals and obtaining independent components, the
second step consists of treating these independent components separately and employing an analytical formula to
them as for monodipole model to get the isolated signal source location for each component.
Keywords: independent component analysis; normal distribution; current dipole; multidipole model; magnetoencephalogram
OBTAINING AN AGGREGATED FORECAST OF RAILWAY FREIGHT
TRANSPORTATION USING KULLBACK–LEIBLER DISTANCE.
- A. P. Motrenko Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, 9 Institutskiy per., Dolgoprudny, Moscow Region 141700, Russian Federation
- V. V. Strijov Dorodnicyn Computing Centre, Russian Academy of Sciences, 40 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Abstract: This study addresses the problem of obtaining an aggregated forecast of railway freight transportation.
To improve the quality of aggregated forecast, the time series clusterization problem is solved in such a way
that the time series in each cluster belong to the same distribution. To solve the clusterization problem, it is
necessary to estimate the distance between empirical distributions of the time series. A two-sample test based on
the Kullback–Leibler distance between histograms of the time series is introduced. Theoretical and experimental
research of the suggested test is provided. Also, as a demonstration, the clusterization of a set of railway time series
based on the Kullback–Leibler distance between time series is obtained.
Keywords: empirical distribution function; distance between histograms; Kullback–Leibler distance; two-sample
problem
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR CORPUS STUDIES:
UNDERPINNINGS FOR CROSS-LINGUISTIC DATABASE CREATION .
- N. V. Buntman Faculty of Foreign Languages and Area Studies, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, 31-a Lomonosov Str., Moscow 119192, Russian Federation
- Anna A. Zaliznyak Institute of Linguistics, Russian Academy of Sciences, 1-1 Bolshyi Kislovskiy pereulok, Moscow 125009, Russian Federation
Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
- I. M. Zatsman Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
- M. G. Kruzhkov Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
- E. Yu. Loshchilova Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str., Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
- D. V. Sitchinava Institute of Russian Language, Russian Academy of Sciences, 18/2 Volkhonka Str., Moscow 119019, Russian Federation
Abstract: Information technology for creation of cross-linguistic databases ofRussian texts with French translations
(also known as parallel texts) is considered. The underlying principles of the developed database provide a unique
combination of three types of bilingual search: lexical, grammatical, and lexico-grammatical. A distinctive feature
of the considered technology is simultaneous creation of Russian-French parallel subcorpus within the National
Russian Corpus and of the cross-linguistic database of Russian verbal lexico-grammatical forms and their French
functional equivalents. The subcorpus and the database have different levels of alignment: the former is aligned
at the level of sentences, and the later at the level of constructions. The academic relevance of the developed
database is due to its support of bilingual contrastive grammar development, as well as to its role in creation of
Russian grammar based on the modern empirical base and information technologies of corpus linguistics. The
main practical application of the database consists in improvement of quality of machine translation.
Keywords: parallel corpus; information technology; cross-linguistic databases; bilingual lexical grammar search;
corpus linguistics; contrastive grammar
CONSTRUCTION OF SYSTEM DYNAMICS MODELS
IN CONDITIONS OF LIMITED EXPERT INFORMATION .
- O. G. Kantor Institute of Social and Economic Researches ofUfa Scientific CentreRAS; 71 Av. Oktyabrya, Ufa 450054, Russian Federation
- S. I. Spivak Bashkir State University, 32 Validy Str., Ufa 450076, Russian Federation
Abstract: System dynamics is a methodology for studying of complex dynamic systems focused on conducting
computer simulations. Construction of system dynamicsmodels is largely dependent on the available experimental
information and expert judgments. A simulation experiment with “bad” models can lead to significant or even
total distortion of the system properties. This paper describes a method of constructing the system dynamics
models, which is a set ofmathematical models, based on the idea of the Kantorovich approach to the mathematical
treatment of experimental data, and computational procedures. An important advantage is the possibility of
including in the model significant conditions which are important to researcher and affect model adequacy. The
developed method was tested on the example of the Russian population.
Keywords: systemd ynamic smodels; point and interval estimation of model parameters; the Kantorovich approach;
the maximum permissible error of measurement
DECLARATIVE KNOWLEDGE STRUCTURES
IN PROBLEM-ORIENTED SYSTEMS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE .
- A. G. Matskevich Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, 44-2 Vavilov Str.,Moscow 119333, Russian Federation
Moscow Technical University of Communications and Informatics (MTUCI), 8a Aviamotornaya Str., Moscow
111024, Russian Federation
Abstract: The article describes the techniques and tools of knowledge representation in the form of declarative
structures based on the Extended Semantic Networks (ESN) formalism to produce intelligent systems knowledge
bases and it provides the examples of intellectual knowledge processing systems for different domains. For processing
the declarative knowledge structures presented in the form of ESN, a specialized logical programming language
DECL has been developed. In DECL, the linguistic processors have been implemented executing translation of
natural language (Russian and English) sentences into structures of a knowledge base, as well as reverse translation
of inner representations into the surface forms of Russian or English.
Keywords: intelligent systems; knowledge representation; natural language processing; semantic networks; logical
programming
UNIVERSAL TECHNOLOGY OF INFORMATION OBJECTS PROXIMITY ASSESSMENT .
- L. A. Kuznetsov Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration (Lipetsk Branch), 3 Internatsional’naya
Str., Lipetskaya oblast, Lipetsk 398050, Russian Federation
Abstract: The paper outlines the technology used to determine the degree of similarity of information objects,
which are represented by text or graphic images. Objects are formalized by probabilistic models. The structure of
the model is set by an algebra on a minimum set of graphic components of an object. Quantitative characteristics
of the structure of objects are the probability distributions on the algebra. The amount of information in objects is
estimated by entropy. The similarity measure of information objects is based on entropy. The paper describes the
method of estimating the proximity of text and graphic objects. The paper provides several examples of estimation
algorithms implementation. It is shown that the developed method is more efficient compared to the methods
described in the literature. The technology used to form images of information objects and to compare their
semantic content is universal. It is possible to adapt the technology to the meaningful characteristics of objects
being analyzed.
Keywords: information object; text; image; probabilisticmodel; semantic similarity; entropy; measure of similarity
|

|



