|

«INFORMATICS AND APPLICATIONS»
Scientific journal
Volume 3, Issue 3, 2009
Content | Bibliography | About Authors
Abstract and Keywords.
MULTICHANNEL QUEUEING SYSTEM WITH REFUSALS OF SERVERS GROUPS.
- A. Pechinkin IPI RAN. apechinkin@ipiran.ru
- I. Sokolov IPI RAN. isokolov@ipiran.ru
- V. Chaplygin IPI RAN. VasilyChaplygin@mail.ru
Abstract: The multichannel queueing system SM/PH/n/r with unreliable servers and their group refusals is under
consideration. The refusals and the restorations of servers groups occur with a constant intensity, the number of
servers refusing simultaneously is a stochastic value, and customers with the interrupted servicing begin its servicing
anew after server restoration. The methods are offered to calculate the stationary distribution of the number of the
customers in the system under different variants of the functioning of the system.
Keywords: multichannel queueing systems; unreliable servers; refusals and restorations of servers groups
ON THE LIMITING CHARACTERISTICS FOR M(t)/M(t)/S QUEUE WITH CATASTROPHES.
- A. I. Zeifman Vologda State Pedagogical University, a_zeifman@mail.ru
- Ya.A. Satin Vologda State Pedagogical University, yacovi@mail.ru
- A. V. Korotysheva Vologda State Pedagogical University, a_korotysheva@mail.ru
- N.A. Tereshina Vologda State Pedagogical University, nataliya_tereshi@mail.ru
Abstract: An M(t)/M(t)/S queue with catastrophes is considered and it is supposed that the catastrophes rates depend on
the length of the queue. Sufficient conditions for weak ergodicity of the respective queue-length process and the
respective bounds are obtained. Some examples are also considered.
Keywords: nonstationary Markovian queueing system; birth and death process with catastrophes; weak ergodicity;
bounds; limiting characteristics; approximation
LARGE DEVIATION ASYMPTOTICS OF STATIONARY QUEUES.
- E. V.Morozov Institute of Applied Mathematical Research, Karelian Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences,
emorozov@krc.karelia.ru
Abstract: The paper is a survey of main asymptotic results playing an important role in the quality of service estimation (QoS)
of stationary systems. The asymptotics of the probability that the workload/queue-size process with heavy tail
exceeds an increasing level is considered. Similar results for the systems with Levy input process and light-tailed
service time are given. The proofs are based on the methods of large deviations theory and illustrated in detail by
theM/M/1 system. The asymptotics of the overflow probability within regeneration cycle is considered, including
the multiserver systems. An asymptotic analysis of system with the long-range dependent input is discussed, with
focus on fractional Brownian process. The ties between the long-range dependence of a queue-size process and the
moment properties of the embedded process of the regenerations are discussed.
Keywords: stationary queue; large deviation probabilities; asymptotic analysis; light-tailed distributions; fractional
Brownian process; long-range dependent process; regeneration
TRAFFIC-LEVEL PROBABILITY MODEL FOR THE NETWORK CENTRIC SYSTEM
- V. Y. Borodakiy National Research Nuclear University “MEPHI”, vladbor@inbox.ru
Abstract: A network centric system model with datacenters serving subscribers’ requests for a data transfer is considered.
Data flows, so called elastic traffic, are characterized by a class independent bandwidth requirement and have
exponentially distributed size. Flow request arriving is modeled by a Poisson process and data flows are served in
accordance with the processor sharing discipline. A single link probability model analysis is presented and the exact
expression of the flow blocking probability is derived.
Keywords: network centric system; elastic traffic; blocking probability; single link
AN APPROACH TO ACTUARIAL MODELING WITH QUASI-MONTE CARLO:
SIMULATION OF RANDOM SUMS DEPENDING ON STOCHASTIC FACTORS.
- G. Temnov Edgeworth Centre for Financial Mathematics, University College Cork, Ireland, g.temnov@ucc.ie
- S. Kucherenko CPSE, Imperial College, London, UK, s.kucherenko@ic.ac.uk
Abstract: The problem of estimating the characteristics of a random sum, when the number of summands is also random, is
addressed. The considered case includes an additional stochastic factor: although the summed random variables
come from a distribution of a known form, the parameters of this distribution are stochastic and can themselves
be viewed as random variables (with known distributions). The Quasi-Monte-Carlo techniques are used to handle
this problem and to analyze its efficiency relative to the regular Monte-Carlo simulation methods. The typical
area of the application of the investigations is actuarial practice which often deals with random sums of financial
losses. Besides actuarial applications, the proposed method may be useful in application to certain problems in
informatics, related to the aggregation of heavy-tailed data.
Keywords: actuarial modeling; quasi-Monte-Carlo simulation; random sums
ON STABILITY OF IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION IN THE PROBLEMS OF EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY.
- O. V. Shestakov Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M. V. LomonosovMoscow State University, oshestakov@cs.msu.su
Abstract: This paper deals with the problem of reconstructing images from projections in emission tomography settings.
Within the frames of given mathematical model, the closeness estimates are derived for reconstructed images when
using finite number of projections.
Keywords: emission tomography; Radon transform; projections; closeness estimates
ON PROBABILISTIC ASPECTS OF ERROR CORRECTION CODES WHEN THE NUMBER OF ERRORS IS A RANDOM SET.
- A.N. Chuprunov Research Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics, Kazan State University, achuprunov@mail.ru
- B. I. Khamdeyev Research Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics, Kazan State University, Khamdeyevbi@mail.ru
Abstract: In the paper, n messages each containing N blocks are considered. Each block is encoded with some antinoise
coding method, which can correct not more than q mistakes. Here, it is assumed that the number of mistakes lies
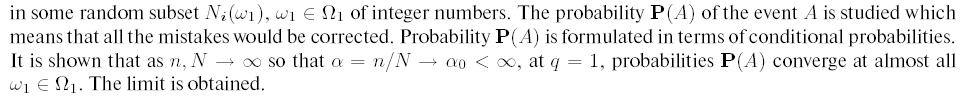
Keywords: generalized allocation scheme; convergence almost sure; Hamming code
ON THE DISTRIBUTION OF PARTICLE SIZE UNDER FRACTURING.
- V.Y. Korolev Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,
M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University; Institute of Informatics Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences
Abstract: A new model for the distribution of particle size under fracturing with the account of nonconstant or random
character of the intensity of the flow of impacts.Within the framework of thismodel, a criterion of the log-normality
of the distribution under consideration is formulated and the class of possible distributions of particle size under
fracturing is described. Along with many known models, this class contains scale mixtures of log-normal laws.
Keywords: log-normal distribution; mixtures of normal distributions; compound Cox process
SOME ESTIMATES FOR CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTIONS WITH AN APPLICATION TO SHARPENING THE MISES INEQUALITY.
- I.G. Shevtsova Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,
ishevtsova@cs.msu.su
Abstract: New estimates are constructed for characteristic functions of distributions with finite absolute moments of order
2 + b, 0 < b < 1. TheMises moment inequality for lattice distributions is also improved.
Keywords: Fourier transform; characteristic function; symmetrization; convolution; lattice distribution; arithmetic
distribution; span
ON THE POWER OF THE TESTS IN THE CASE OF GENERALIZED LAPLACE DISTRIBUTION.
- V.E. Bening Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M. V. LomonosovMoscow State University,
bening@yandex.ru
- O.O. Lyamin Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M. V. LomonosovMoscow State University
Abstract: In the paper, the formula for the normalized limit difference between the power of asymptotically most powerful
test and that of a locally most powerful test in the case of the generalized Laplace distribution is obtained.
Keywords: generalized Laplace or generalized double exponential distribution; power function; deficiency;
asymptotic expansion
|

|