“Informatics and Applications” scientific journal
Volume 4, Issue 3, 2010
Content
Abstract and Keywords
About Authors
ESTIMATION OF SELF-HEALING TIME FOR DIGITAL SYSTEMS UNDER TRANSIENT FAULTS.
- S. L. Frenkel Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Slf-ipiran@mtu-net.ru
- A. V. Pechinkin Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences, apechinkin@ipiran.ru
Abstract: This paper suggests a new approach to self-healing property prediction for digital systems. Self-healing refers to the system’s ability to continue operating properly in the case of the failure of some of its components.
This phenomenon is very considerable aspect of high-reliable systems design. The self-healing time characteristics
are analyzed during design process, and the computation of probability distribution function of self-healing time
needs for fair prediction of real time systems reliability. This paper considers the possible ways of estimation of time to self-healing under transient faults using a Markov model of a design behavior for reliability analysis of digital
systems with some fault-tolerant properties, modeled by the well-known Finite State Machine formalism.
Keywords: fault-tolerant computer; self-healing fault-tolerance; transient faults; finite state machine; Markov chains
ON STABILITY FOR NONSTATIONARY QUEUEING SYSTEMSWITH CATASTROPHES.
- A. I. Zeifman Vologda State Pedagogical University; IPI RAN; VSCC CEMI RAS, a_zeifman@mail.ru
- A. V. Korotysheva Vologda State Pedagogical University, a_korotysheva@mail.ru
- Ya.A. Satin Vologda State Pedagogical University, yacovi@mail.ru
- S. Ya. Shorgin IPI RAN, SShorgin@ipiran.ru
Abstract: Nonstationary birth and death processes (BDPs) with catastrophes are considered. The bounds of stability for some characteristics of such systems are obtained. Also, a queueing example is considered.
Keywords: nonstationary queues; Markovian models with catastrophes; stability; bounds; limiting characteristics;
approximations
BAYESIAN QUEUEING AND RELIABILITYMODELS: CHARACTERISTICS OF MEAN NUMBER
OF CLAIMS IN THE SYSTEM 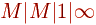 . .
- A.A. Kudriavtsev Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, nubigena@hotmail.com
- S. Ya. Shorgin IPI RAN, SShorgin@ipiran.ru
Abstract: The paper is a continuation of the series of papers devoted to Bayesian queuing and reliability models investigation.
The probability characteristics of mean number of claims in the system 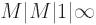 under conditions of input flow
and service parameters randomization are considered. The paper includes the discussion of the obtained results
interpretation taking into account that the mean number of claims distribution may be improper. under conditions of input flow
and service parameters randomization are considered. The paper includes the discussion of the obtained results
interpretation taking into account that the mean number of claims distribution may be improper.
Keywords: Bayesian approach; queueing systems; reliability; mixed distributions; modeling; improper distribution; "defective" distribution
QUEUEING SYSTEMS WITH MINIMIZED AVERAGE WAITING LINE.
- S. S.Matveeva Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, petkin@mail.ru
- T. V. Zakharova Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, lsa@cs.msu.su
Abstract: A research of the properties of optimal arrangements is made in accordance with the average waiting line criteria in space for systems with FIFO service discipline. A stream of the homogeneous requirements differing only by the moments of receipt in system is considered. The service centers are being like M|G|1 systems. The properties of optimal arrangements are described and the algorithms for constructing asymptotically optimal arrangements, minimizing the optimal criteria are presented.
Keywords: asymptotically optimal arrangements; average waiting line; criterion of optimality
ON ESTIMATION OF THE LARGE DEVIATION ASYMPTOTIC OF A SINGLE SERVER REGENERATIVE STATIONARY QUEUE.
- A. V. Borodina Institute of Applied Mathematical Research, Karelian Research Centre RAS, borodina@krc.karelia.ru
- E. V.Morozov Institute of Applied Mathematical Research, Karelian Research Centre RAS, emorozov@krc.karelia.ru
Abstract: The (small) probabilities estimation of such undesirable events like loss/collapse of data, buffer overflow, collision
of packets in the modern telecommunication systems by classical methods requires unacceptable large time and
computational efforts. However, exact analytical results are known only for a narrow class of queues and queueing
networks. It calls a necessity to develop both asymptotic methods of analysis and speed up simulation to estimate
the probabilities of this type. In this paper, a speed-up simulation method based on the splitting of the trajectories of
a regenerative process developed by the authors is applied to estimation of the overflow probability for a stationary
workload/queue-size process. It allows to simplify and accelerate considerably the estimation of the exponent in
the asymptotic representation of the large deviation probability provided that service time has a finite moment
generating function (the so-called light tail). Numerical simulation results are presented.
Keywords: large deviation asymptotic; single-server system; stationary waiting time; splitting method; accelerated simulation
SEARCH OF THE CONFLICTS IN SECURITY POLICIES: A MODEL OF RANDOM GRAPHS.
- A.A. Grusho Department of Computer Security, Faculty of Information Protection, Institute of Information Sciences and Security Technologies, Russian State Humanitarian University; Department of Mathematical Statistics, Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, grusho@yandex.ru
- N.A. Grusho Department of Computer Security, Faculty of Information Protection, Institute of Information Sciences and Security Technologies, Russian State Humanitarian University, grusho@yandex.ru
- E. E. Timonina ĐDepartment of Fundamental and Applied Mathematics, Institute of Information Sciences and Security Technologies, Russian State Humanitarian University, eltimon@yandex.ru
Abstract: Risk analysis requires at least a rough estimate of the probability of problematic situations in the implementation
of security policy. Such estimates can be obtained in the analysis of conflicts in security policies using models of
random graphs. In this paper, two examples of conflicts in security policy are considered and a model of random
graphs for their research is constructed. The results of analysis were used to evaluate the influence of certain
parameters of random graphs on the probability of the existence of conflicts and complexity of search algorithms in
real conflict security policies.
Keywords: security policy; threats to information security; mathematical models of security policy
LAWS OF ITERATED LOGARITHM FOR NUMBERS OF NONERROR BLOCKS UNDER ERROR CORRECTED CODING.
- A.N. Chuprunov Department of Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Chebotarev Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics, Kazan State University, achuprunov@mail.ru
- I. Fazekas Faculty of Informatics, University of Debrecen, Hungary, fazekasi@inf.unideb.hu
Abstract: Messages containing blocks are considered. Each block is encoded with some antinoise coding method, which can correct not more than r mistakes. It is assumed that the number of mistakes in a block is a nonnegative integer
valued random variable. The random variables are independent and identically distributed. Also, it is assumed that
the number of mistakes in a message belongs to a some finite set of integer numbers. In the paper, the analogs of
the Law of Iterated Logarithm for a number of nonerror blocks in a message is proved.
Keywords: generalized allocation scheme; conditional probability; conditional expectation; exponential inequality; Law of Iterated Logarithm; Hamming code
ON AN ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF POWER OF TESTS IN CASE OF GENERALIZED LAPLACE DISTRIBUTION.
- ÎO.O. Lyamin Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, oleg.lyamin@gmail.com
Abstract: In paper by Bening and Lyamin (INFORMATICS AND APPLICATIONS, 2009, vol. 3, issue 3, pp. 79-88), a formula for a
limit of deviation of power of the asymptotically most powerful test from power of the most powerful test in case of
generalized Laplace distribution was heuristically obtained. In the present paper, a formal proof of this formula is
derived.
Keywords: generalized Laplace distribution; power function; asymptotically most powerful test; asymptotic expansion
SOME ISSUES OF TECHNOLOGY SELECTION TO BUILD VISUALIZATION SYSTEM IN SITUATIONAL CENTER.
- A.A. Zatsarinny IPI RAN, AZatsarinny@ipiran.ru
- K.G. Chuprakov IPI RAN, chkos@rambler.ru
Abstract: The main steps of visualization systems selection in situational centers are shown. An accent is made on a step
devoted to describing technology selection. Displaying technologies used in situational centers are considered. The
authors suggest themain parameters of visualization systemand amethodological approach to technology selection
using approach of exclusion by parameters.
Keywords: visualization systems; situational center; displaying technology; selection problem; exclusion approach
COGNITIVE LINGUISTIC PRESENTATIONS IN THE TEXT PROCESSING SYSTEMS.
- E. B. Kozerenko IPI RAN, kozerenko@mail.ru
- I. P. Kuznetsov IPI RAN, igor-kuz@mtu-net.ru
Abstract: The paper deals with the issues of design and development of syntactic semantic and lexical semantic presentations
in linguistic processors of the systems based on the Extended Semantic Networks mechanism. The systems of this
class are developed for knowledge extraction from natural language texts and mapping the extracted entities and
relations into the knowledge base structures for further use by experts in application areas. This paper focuses on
the cognitive linguistic solutions employed for constructing an integral linguistic model which can be modified
depending on the specific task, and which range from the "heavy" form based on the specific deep presentations to
the reduced shells focused on a particular subject area and the controlled language. Special attention is given to the
techniques of describing the distributional and transformational features of language objects.
Keywords: intelligent systems; semanticpresentations; linguisticprocessors; natural languageprocessing; knowledge
mining
TYPOLOGY AND COMPUTER MODELING OF TRANSLATION DIFFICULTIES.
- N. Buntman Faculty of Foreign Languages and Area Studies at Moscow State University, nabunt@hotmail.com
- J.-L.Minel Universit‚e Paris Ouest Nanterre La D‚efense, jean-luc.minel@u-paris10.fr
- D. Le Pesant Universit‚e Paris Ouest Nanterre La D‚efense, denis.lepesant@wanadoo.fr
- I. Zatsman Institute of Informatics Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences, iz_ipi@a170.ipi.ac.ru
Abstract: The problem of generating of goal-oriented knowledge systems in linguistics is reviewed. The problem belongs to a new research area, which is called “cognitive informatics.” The article focuses on computer coding of goal-oriented knowledge systems using as an example the typology of Russian-to-French translation difficulties.
Keywords: time-dependent semiotic model; goal-oriented knowledge systems in linguistics; denotata; concepts; information objects; computer codes
|



